The development of robots for maintenance tasks has been a promising area of technological advancement in recent years. Engineers have been able to create a variety of robots capable of assisting in the maintenance and repair of infrastructure. However, a common limitation of many of these robots is the need for external power sources, which restricts their practical application in real-world scenarios. Recently, researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems, Harbin Institute of Technology, and Hong Kong University of Science and Technology have introduced a new wireless miniature robot that can navigate through pipes and other tubular structures without relying on external power sources.
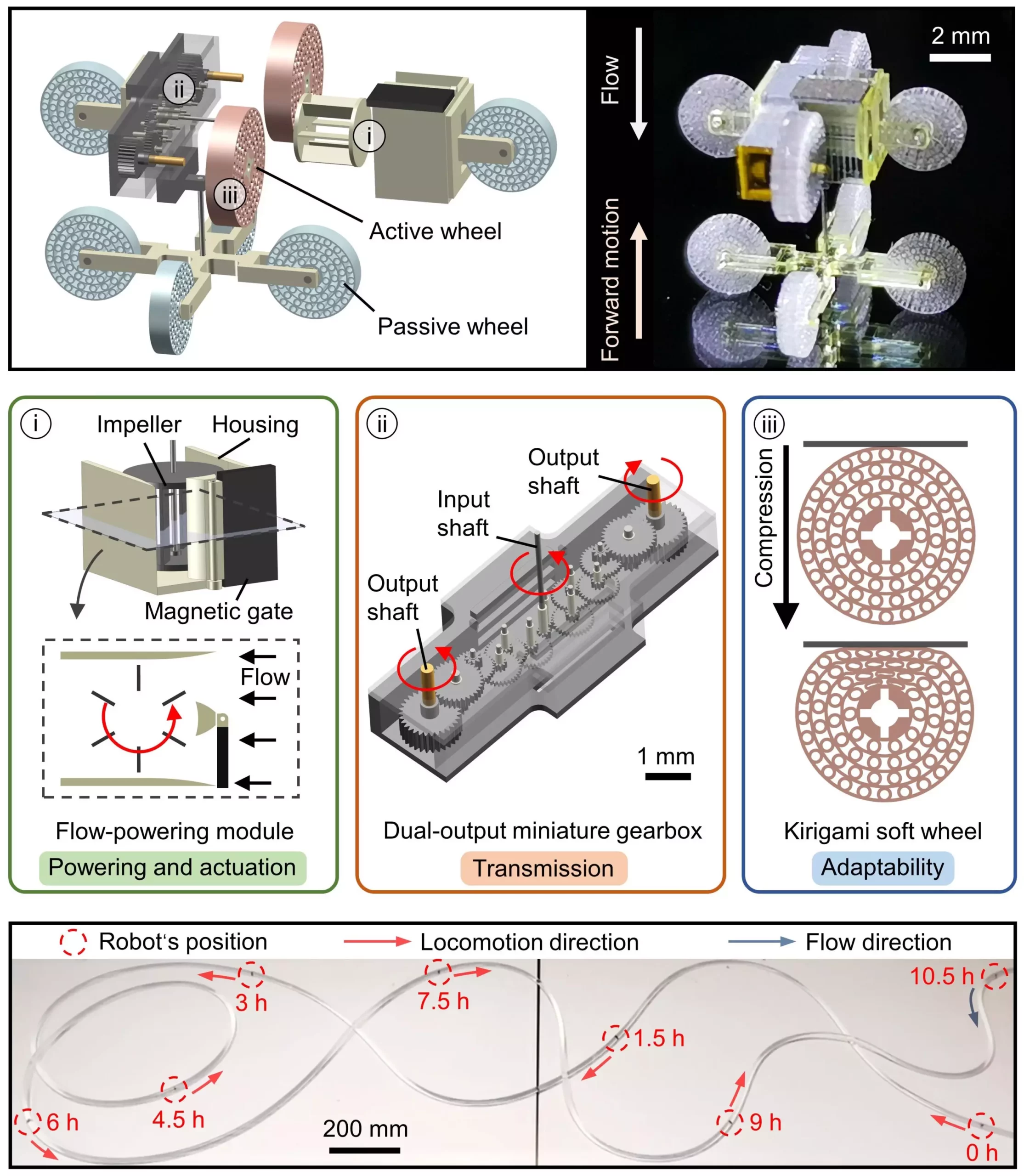
The wireless millimeter-scale robot developed by this team offers a solution to the challenges faced by traditional maintenance robots. Unlike larger robots that rely on external power sources and have limited functionality, this innovative robot includes an internal power source and an actuation unit. This design allows the robot to utilize its available energy in a controlled manner, enabling it to cover longer distances within tubular structures and perform routine maintenance tasks for extended periods without running out of power.
Key Components
The robot incorporates three key components: a flow-powering module, a dual-output miniature gearbox, and kirigami soft wheels. The flow-powering module converts the flow of fluids in tubular structures into mechanical energy, while the gearbox transmits this energy to the robot’s locomotion system. The addition of kirigami soft wheels enables adaptive locomotion in complex tubes, giving the robot the ability to navigate through a variety of environments.
Potential Applications
The capabilities of this wheeled millimeter-scale robot are diverse and promising. It can navigate through tubular structures filled with flowing gases or liquids, making it ideal for applications in industries such as nuclear, industrial, and medical. The robot’s direction of movement can be easily controlled by applying an external magnetic field, further enhancing its versatility in different scenarios.
The researchers have conducted preliminary tests on the robot and obtained encouraging results. Moving forward, their focus is on enhancing the robot’s capabilities and stability to prepare it for deployment in real-world settings. Strategies such as streamlining the robot’s body to minimize flow resistance or adding microstructures to the wheel surfaces to increase friction are being considered to improve its performance in challenging environments. Additionally, advancements in the use of external magnetic fields for motion status switching are being explored to expand the robot’s operational range.
The development of wireless millimeter-scale robots represents a significant advancement in the field of maintenance robotics. By overcoming the limitations of traditional maintenance robots, these innovative robots have the potential to revolutionize maintenance tasks in a variety of industries. With ongoing research and development efforts focused on enhancing their capabilities, these robots are set to play a crucial role in the future of maintenance technology.

Leave a Reply