Wireless internet has become an essential part of our daily lives, enabling us to stay connected, browse the internet, and stream media content. With the increasing demand for wireless internet access, there is also a surge in power consumption, leading to a rise in carbon emissions globally. To address this issue, researchers are now focusing on developing energy-efficient techniques to support communication between devices and the sharing of information online.
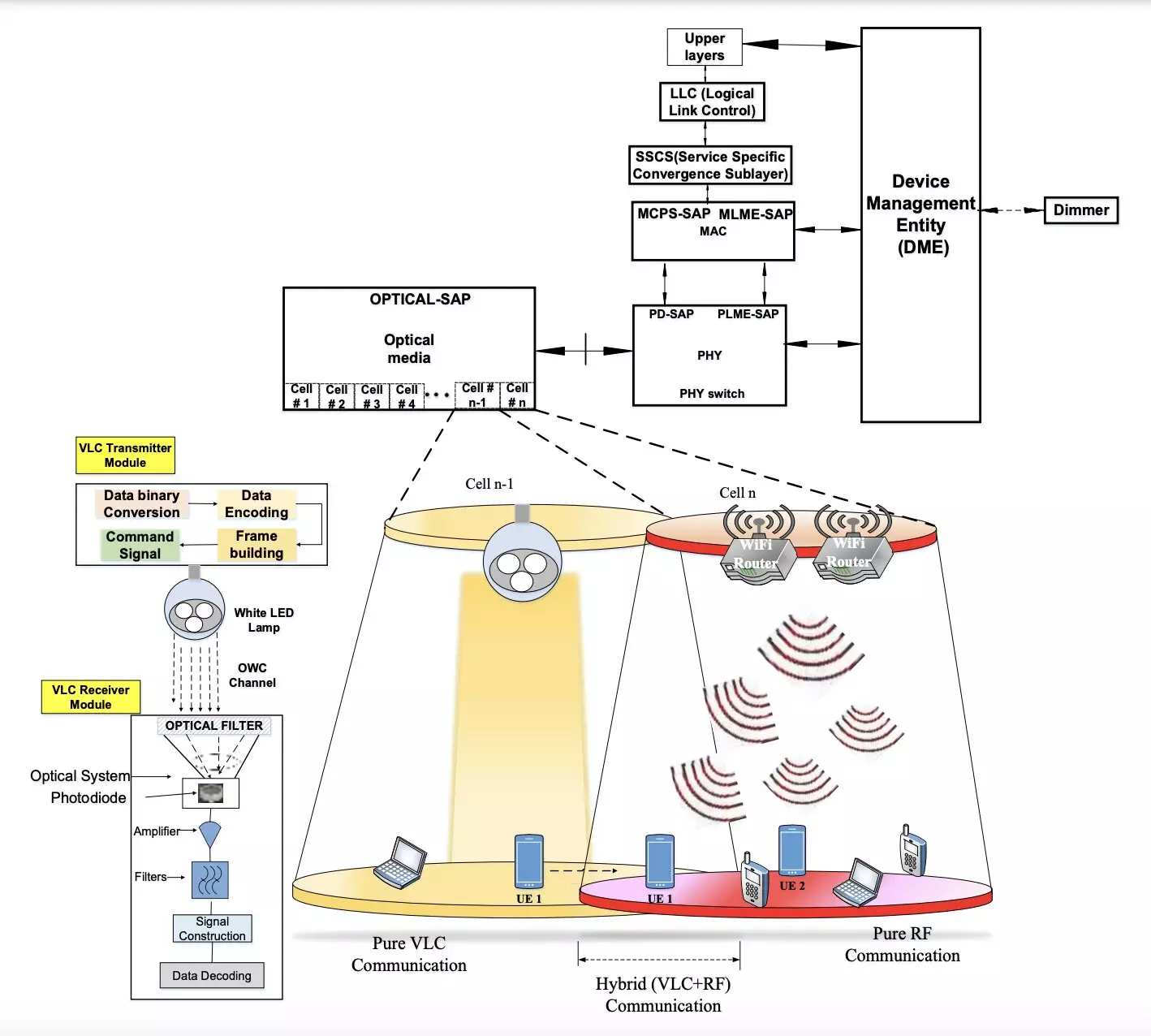
One of the innovative solutions that researchers are exploring is Visible Light Communication (VLC). VLC is a method that utilizes visible light, such as light-emitting diodes (LEDs), to transmit data wirelessly. Recently, a team of researchers from Central University, IIDM, and CU J&K in India has developed a new hybrid approach that combines VLC with Radio Frequency (RF) communication. This hybrid solution, as outlined in a paper published in IEEE Transactions on Green Communications and Networking, aims to provide reliable communication in indoor environments with high data transmission rates while consuming less energy.
The wireless communication system proposed by the research team consists of two main components: a transmitter and a receiver module. These modules are physically separated but connected via a VLC channel. The transmitter sends binary data in the form of LED-produced light, while the receiver, equipped with a photosensitive device, extracts the transmitted information when in the line of sight. The use of modulation schemes helps maintain a continuous data stream while keeping power consumption constant throughout the communication process.
The researchers conducted an initial evaluation of their hybrid wireless communication system using various simulation platforms. Their findings indicate that the system enables stable communication between devices in indoor environments with significant energy savings. By comparing RF communication, a hybrid of RF and VLC, and pure VLC, the team demonstrated high energy efficiency, lower Specific Absorption Rate (SAR), and enhanced battery lifetime for mobile devices. These results validate the potential of the proposed hybrid approach in reducing power consumption and improving wireless communication efficiency.
The study by the research team contributes to the ongoing efforts to enhance energy efficiency and reduce electromagnetic radiation in wireless communications. The promising results from their simulations suggest that the hybrid approach could be further refined and tested in future studies. By integrating VLC with RF communication, the researchers have laid the groundwork for a more sustainable and energy-efficient wireless communication system that could benefit both users and the environment.

Leave a Reply