In a groundbreaking development, a team of Korean researchers led by Professor Shinhyun Choi has introduced a new memory device with the potential to revolutionize existing memory technologies. This innovative device is not only cost-effective but also boasts ultra-low power consumption, making it a promising candidate for future artificial intelligence hardware.
The existing phase change memory technology faces significant challenges, including expensive fabrication processes and high power consumption. These drawbacks have limited the practicality of implementing phase change memory in large-capacity memory products and neuromorphic computing systems. In response to these challenges, Professor Choi’s research team set out to develop a solution that overcomes these obstacles.
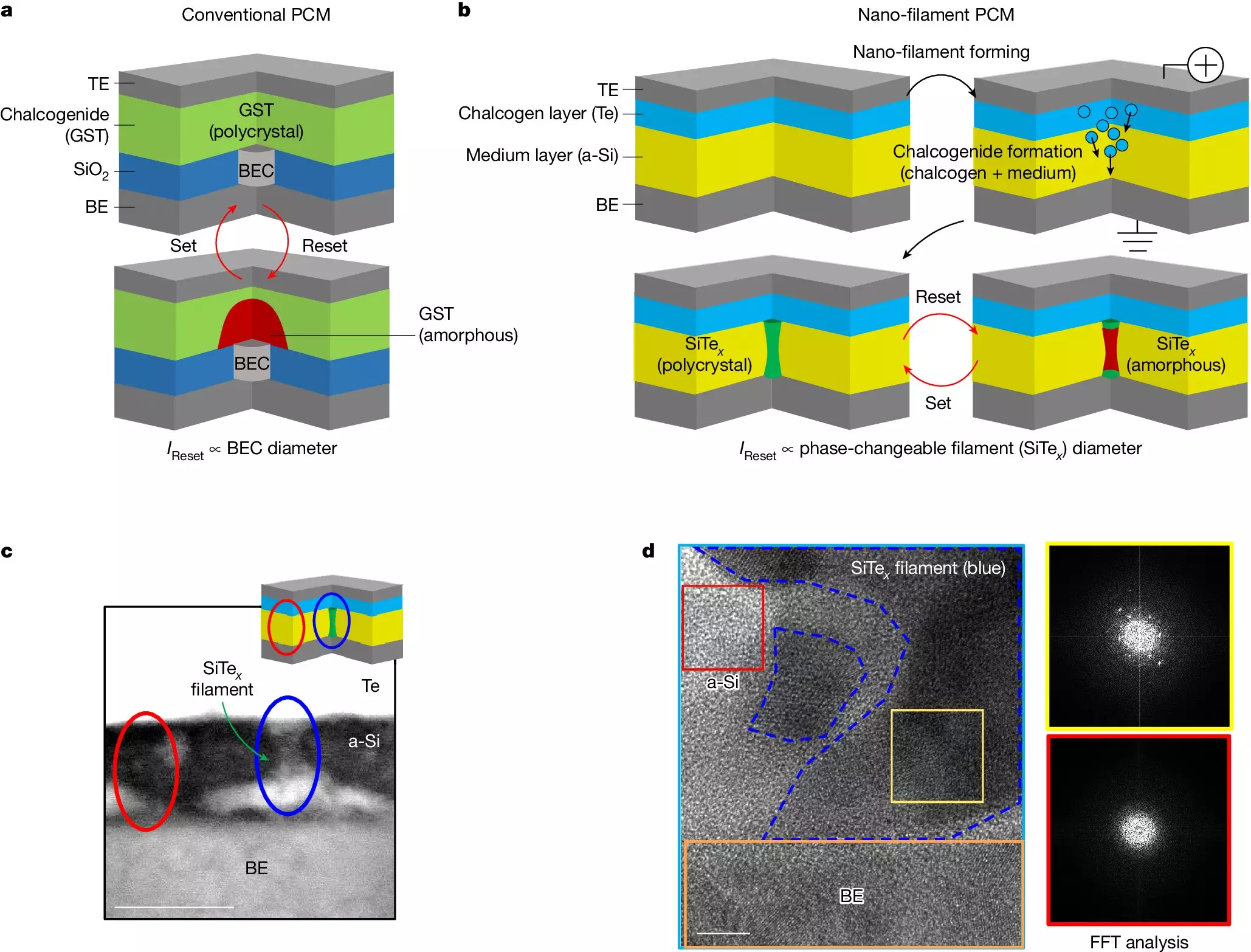
A New Approach
The key breakthrough in this research lies in the creation of an ultra-low–power phase change memory device that forms a nanometer-scale phase-changeable filament without the need for costly manufacturing processes. By focusing on maximizing thermal efficiency and reducing power consumption, the team was able to achieve a device that consumes 15 times less power than conventional phase change memory devices.
Advantages over Existing Memory Technologies
The newly developed memory device offers a unique combination of high speed and non-volatile characteristics, which are essential for next-generation memory systems. Unlike DRAM, which is fast but volatile, and NAND flash memory, which is slower but non-volatile, the phase change memory device bridges the gap between these two technologies, offering the best of both worlds.
With the successful development of this ultra-low–power phase change memory device, Professor Shinhyun Choi’s research team has paved the way for a new era in memory technology. By addressing the issues of high power consumption and expensive fabrication processes, this breakthrough opens up new possibilities for the widespread adoption of phase change memory in diverse applications.
The new memory device developed by the Korean research team represents a significant advancement in memory technology. With its low processing costs, ultra-low–power consumption, and ability to replace existing memory technologies, this device is poised to reshape the landscape of artificial intelligence hardware and computing systems. As research in this field continues to progress, we can look forward to further innovations and advancements that will drive the future of memory technology forward.

Leave a Reply