The recent study conducted by researchers at Aalto University in Finland has shed new light on the use of magnets to control the movement of bacteria. While the findings are intriguing and pose significant implications for various research fields, it is crucial to critically evaluate the methodology, results, and potential applications of this study.
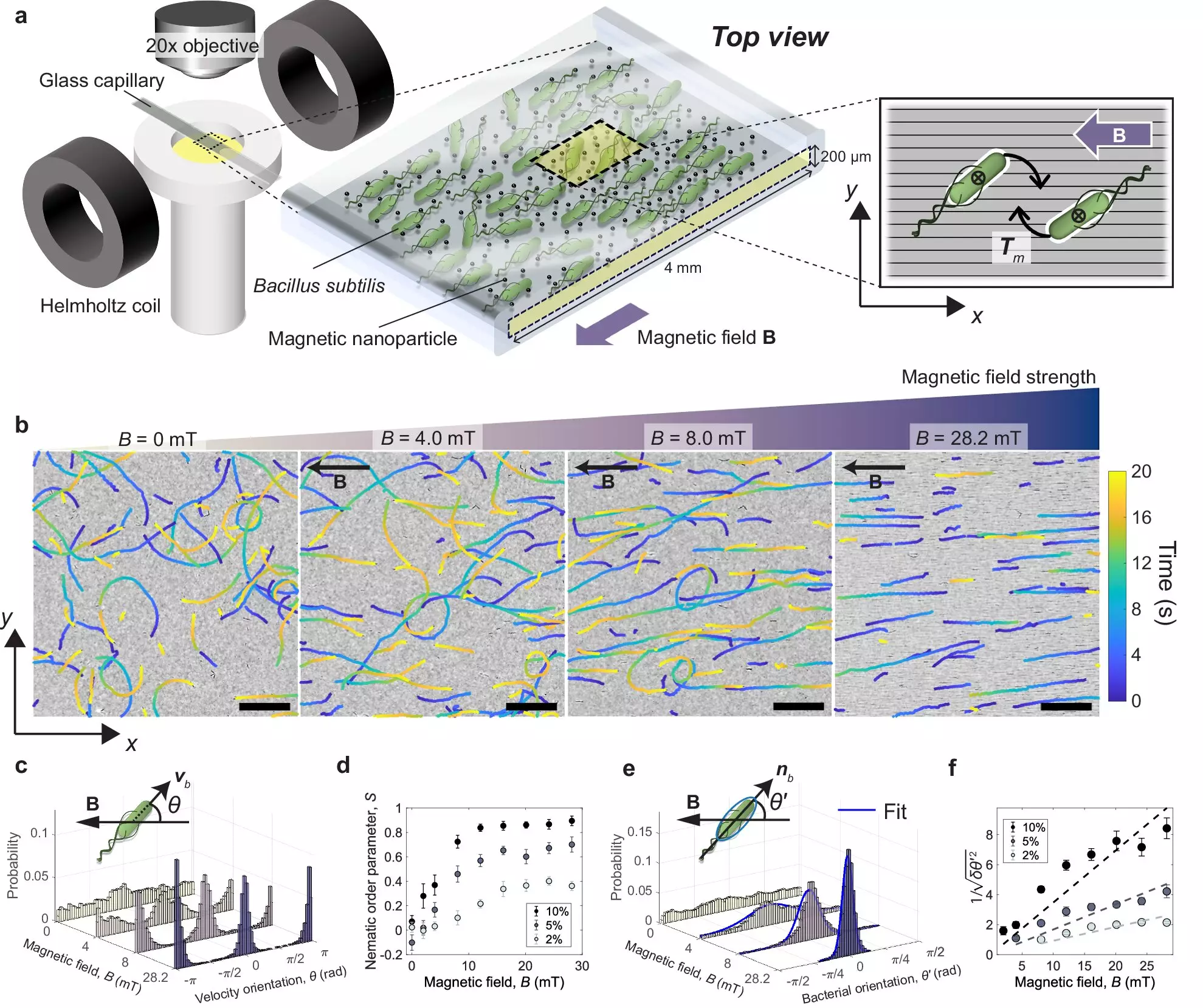
The approach of using magnets to align bacteria as they swim is innovative and offers a unique way to manipulate bacterial behavior. However, the researchers primarily focused on controlling the bacteria’s alignment through the magnetic field without delving into the potential impacts of the magnetic nanoparticles in the surrounding fluid. Further investigation into how these nanoparticles may interact with the bacteria or influence their behavior would provide a more comprehensive understanding of this system.
The study demonstrates that the strength of the magnetic field directly influences the alignment of bacteria, with higher field strengths resulting in more structured and organized bacterial movement. While this is a promising outcome, the researchers should have explored the long-term effects of prolonged exposure to magnetic fields on bacterial viability and health. Additionally, the implications of active turbulence in dense bacterial suspensions could have been further elucidated to provide a deeper insight into this phenomenon.
The researchers rightly point to the potential applications of this study in the fields of active matter physics, targeted drug delivery, microrobotics, and biological engines. However, a more detailed discussion on the practical implementation of these findings in real-world scenarios would have been beneficial. Furthermore, the proposal to investigate dynamic magnetic fields in future experiments is promising, but the potential risks and limitations associated with this approach need to be carefully considered.
One aspect that the researchers overlooked is the ethical implications of manipulating bacterial behavior using external forces. While the study’s focus was on scientific advancement and understanding active matter, the broader ethical implications of controlling living organisms with artificial means should not be ignored. Future research should incorporate ethical frameworks to ensure the responsible use of such technology.
While the study by Aalto University researchers presents an exciting development in the field of bacterial control using magnets, there are several areas that require further exploration and critical evaluation. By addressing methodological limitations, analyzing results comprehensively, considering ethical implications, and exploring practical applications, future research in this area can unlock the full potential of controlling bacterial movement for various scientific and technological advancements.

Leave a Reply