The advancements in robotics have opened up a world of possibilities for integrating robots into various environments to assist humans in performing tasks efficiently. While robotic systems have traditionally been used indoors for tasks like warehouse management and customer service, a new frontier is emerging that involves utilizing robots in outdoor environments. However, outdoor environments present unique challenges, such as unknown and occluded regions, which can impede the navigation of robots and increase the risk of collisions.
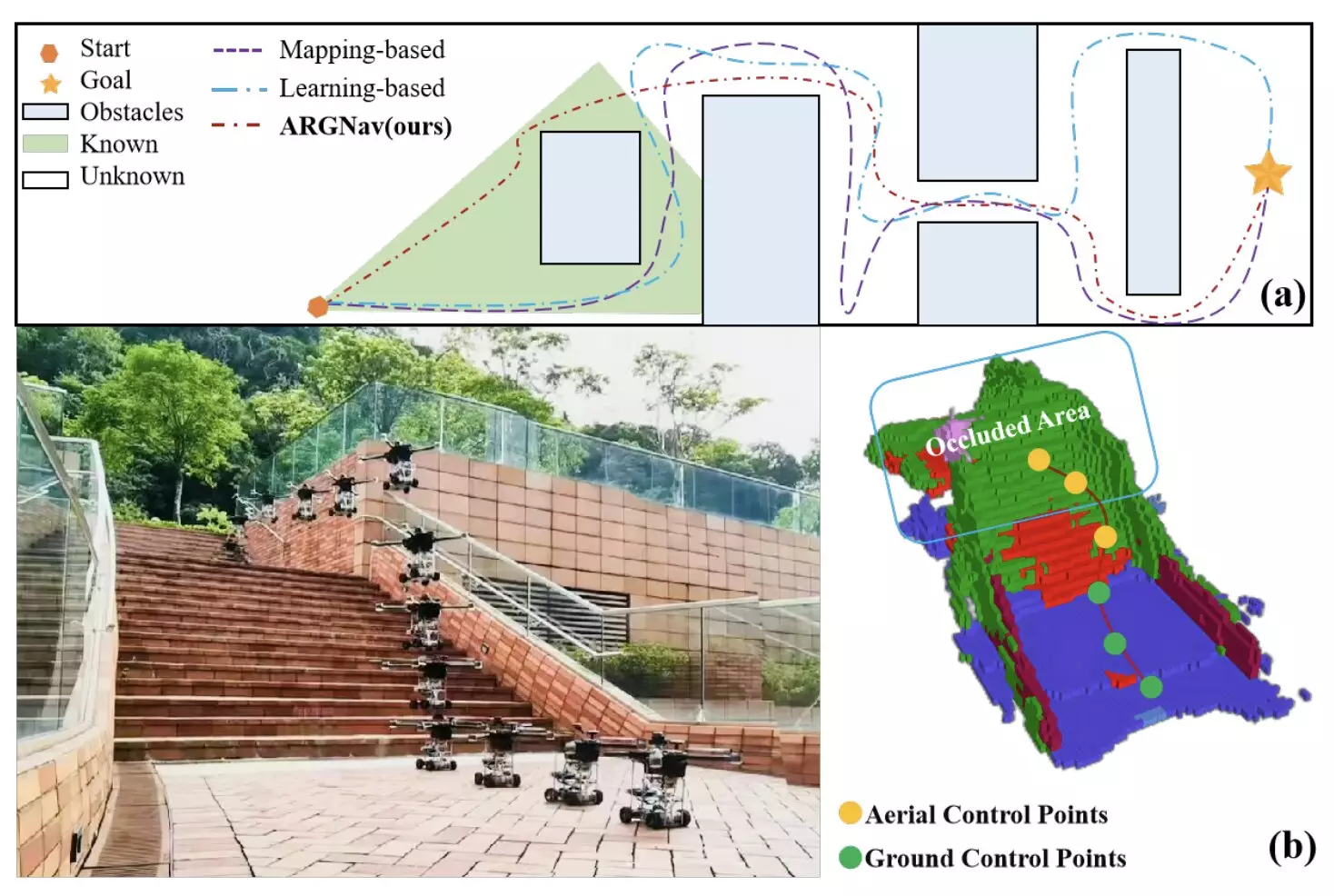
Researchers at the University of Hong Kong have made significant strides in addressing the challenges of navigating air-ground robots in occlusion-prone environments. Their groundbreaking framework, known as AGRNav, combines a lightweight semantic scene completion network (SCONet) and a hierarchical path planner to enhance the autonomous navigation of robots. By accurately predicting obstacles in the environment and planning energy-efficient paths, AGRNav aims to revolutionize the way robots navigate complex outdoor settings.
The key components of AGRNav – SCONet and the hierarchical path planner – work in synergy to enable robots to navigate challenging environments effectively. The SCONet utilizes a deep learning approach to predict the distribution of obstacles and their semantic features, providing crucial information for path planning. On the other hand, the hierarchical path planner leverages the predictions from SCONet to chart optimal aerial and ground paths for the robot to reach its destination efficiently.
The researchers conducted extensive simulations and real-world experiments to evaluate the performance of AGRNav in different environments. They tested the framework on a customized air-ground robot and found that it outperformed existing navigation frameworks in terms of identifying optimal and energy-efficient paths. This validation underscores the effectiveness of AGRNav in enhancing the navigation capabilities of air-ground robots in occlusion-prone environments.
One of the key advantages of AGRNav is its open-source nature, allowing developers worldwide to access and utilize the framework for their own projects. The availability of AGRNav on GitHub opens up opportunities for further research and collaboration in the field of robotics. Moving forward, the researchers envision deploying AGRNav on other air-ground robotic platforms to assess its effectiveness in real-world scenarios and contribute to the advancements in robotic navigation technology.
AGRNav represents a significant advancement in the field of robotic navigation, particularly in challenging outdoor environments. The collaborative efforts of the research team at the University of Hong Kong have resulted in a novel framework that holds immense potential for revolutionizing the way air-ground robots navigate complex and occluded settings. With its innovative approach and promising results, AGRNav is poised to pave the way for the next generation of autonomous robotic systems.

Leave a Reply