Northern Europe is currently experiencing relatively warm temperatures compared to other regions on the same latitude, such as major Canadian cities. London, for example, is warmer than cities like Vancouver, thanks in part to the Atlantic Meridional Ocean Current (AMOC). This current carries warm water from the Gulf of Mexico to northern Europe, keeping ports ice-free. However, with the effects of global warming, the AMOC is at risk of collapsing by the turn of the century. The influx of freshwater from the melting Arctic and increased rainfall due to global warming could disrupt the current’s flow, ultimately leading to a decrease in warmth in northern Europe.
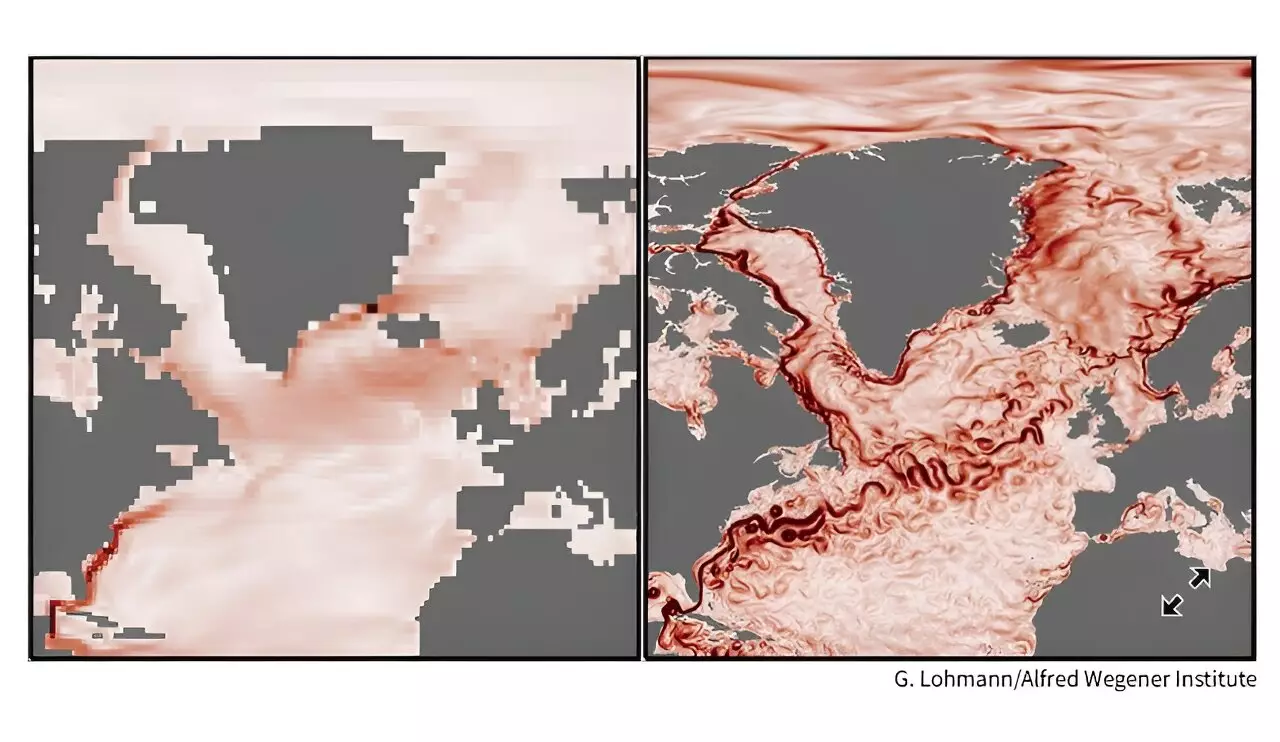
Climate models have been crucial in predicting the potential collapse of the AMOC. However, until recently, these models have not been able to provide a detailed analysis of the current’s behavior. New high-resolution climate models, such as the Community Earth System Model, now offer a more nuanced view of the AMOC’s future. These models have allowed scientists to uncover unexpected variations in the current’s strength and direction. With a more detailed examination of the AMOC, researchers can now make more accurate forecasts about its potential collapse and impact on regional climate.
The latest climate models have revealed regional variations in the AMOC that were previously unknown. These variations include tipping points, where small changes can lead to abrupt shifts in the current’s behavior. Just as a slight increase in temperature can cause an ice sheet to melt rapidly, the AMOC also has tipping points that could have far-reaching consequences. By incorporating these localized dynamics into future forecasts, scientists hope to better understand the potential impacts of an AMOC collapse on climate and marine ecosystems. The feedback between the overall AMOC and smaller-scale variations could also play a critical role in shaping future climate patterns.
As researchers continue to study the AMOC and its potential collapse, it is clear that urgent action is needed to address the impacts of global warming on ocean currents. By advancing climate models and incorporating regional dynamics into forecasts, scientists hope to anticipate and respond to dramatic changes in our planet’s systems. The findings from these studies underscore the critical importance of understanding the complexities of the AMOC and its interactions with other climate systems. With the future of the AMOC hanging in the balance, it is essential to prioritize research and mitigation efforts to safeguard the stability of our planet’s climate.

Leave a Reply