As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources, tidal power emerges as a critical player in the quest for sustainable solutions. With the tides being one of the most predictable natural phenomena, the United Kingdom’s coastline is poised for significant growth in tidal energy installations. This shift comes in response to the pressing need to transition to cleaner energy alternatives amidst climate change concerns. Yet, harnessing tidal energy is not without its hurdles. The introduction of advanced turbine technologies into tumultuous marine environments poses substantial challenges, requiring extensive research to mitigate risks related to ecological interactions and turbine performance.
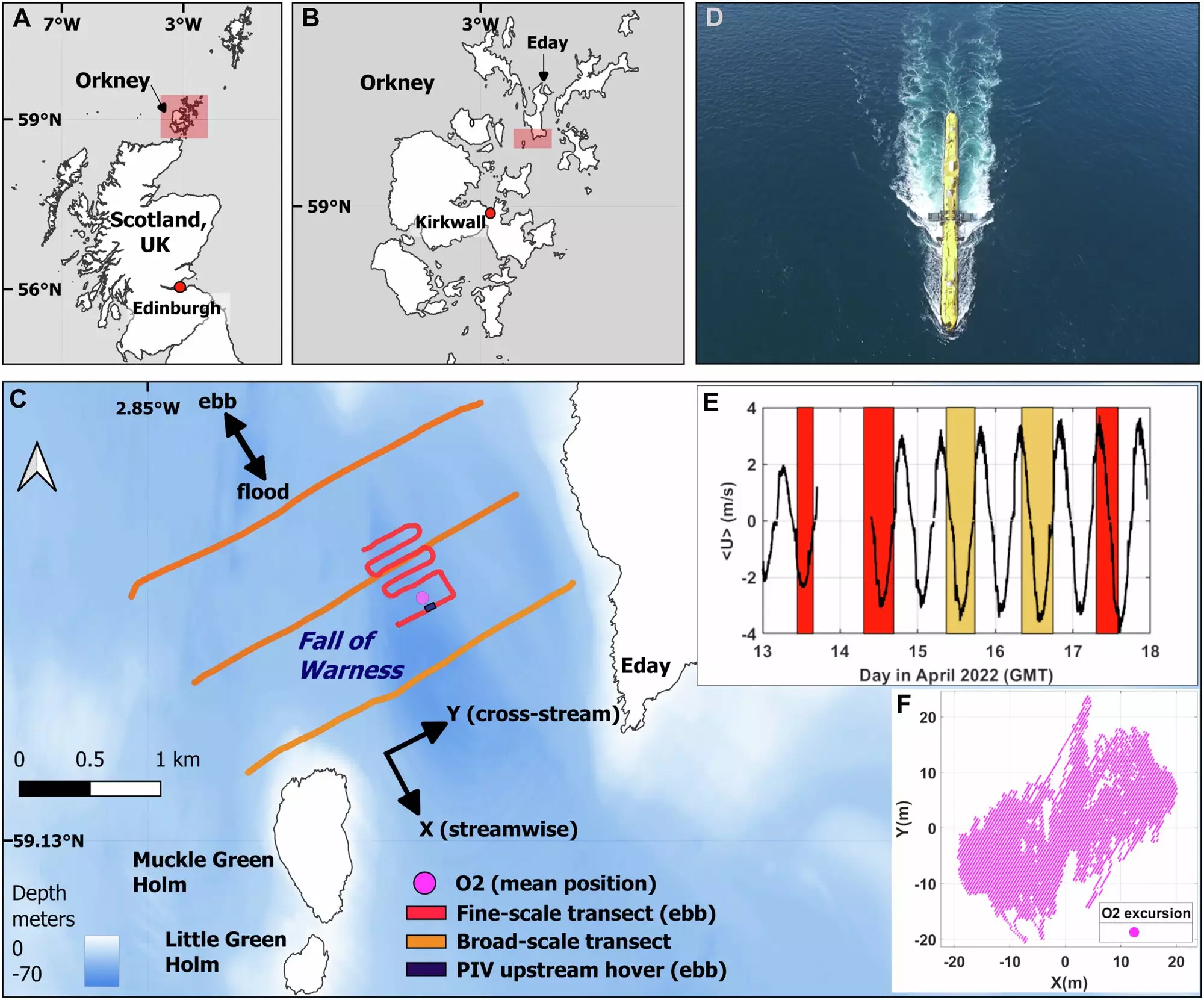
One primary challenge faced by the tidal energy sector is the unpredictable nature of tidal flows. Scientists have recently made strides in addressing this issue, particularly concerning one of the most powerful tidal turbines in the world, Orbital Marine Power’s O2. This floating turbine, anchored to the seabed, capitalizes on the kinetic energy of moving water to generate electricity—potentially powering about 2,000 homes. However, real concerns arise regarding how these devices will perform in waters where tidal currents exceed 8 knots. The wake produced by the turbine not only affects its own performance but has broader implications for the placement of additional turbines and the surrounding marine habitats.
Innovative research methods, including aerial drone surveys and boat-based assessments, have been pivotal in mapping the complex tidal dynamics surrounding the O2 turbine. This cutting-edge approach enables scientists to gather valuable data that can inform the optimal siting of tidal turbines, thereby maximizing their energy generation potential while minimizing ecological disruption.
The ecological impact of tidal turbines cannot be overstated. A previous study revealed that the wake generated by the O2 turbine attracted breeding seabirds, creating a foraging hotspot. However, when turbine arrays are densely packed, it could lead to unintended consequences by restricting the movement of marine fauna. In one instance, researchers even observed orcas passing near the turbine during drone surveys, underscoring the need to carefully evaluate the effects of tidal installations on local wildlife.
As the momentum for tidal energy grows, understanding the interactions between these technologies and marine ecosystems is imperative. This knowledge not only ensures the sustainability of marine environments but also supports the public’s acceptance of renewable energy initiatives. Therefore, site-specific assessments must become standard practice to guarantee that tidal energy development does not come at the expense of ecological balance.
The research conducted by a collaboration between institutions such as the Marine Biological Association, the University of Plymouth, and the University of the Highlands and Islands emphasizes the importance of merging scientific expertise with innovative technologies. By embracing a methodical approach to studying dynamic tidal environments, significant strides can be made toward facilitating the sustainable development of tidal energy systems.
Experts like Dr. Lilian Lieber stress that the current study’s findings open up possibilities for better decision-making when it comes to placing turbines in challenging tidal flows. The exploration of real-world conditions versus laboratory simulations can provide insights crucial for tackling the complexities associated with tidal energy generation.
Despite the advancements being made, the tidal energy sector faces considerable hurdles. Key challenges such as the costs associated with scaling up technology, ensuring effective grid connections, and maintaining turbine functionality in turbulent environments remain at the forefront of industry discussions. Effective collaboration among researchers, stakeholders, and local communities will be critical to overcoming these challenges.
The potential for tidal energy in the UK is considerable, with studies suggesting that it could meet up to 11% of the nation’s electricity needs. As the UK aspires to blend its energy portfolio, harnessing tidal power poses an opportunity to contribute significantly to energy independence and sustainability.
As we venture into an era marked by a more aggressive shift to renewable sources, tidal energy stands as a beacon of hope. The challenges are non-trivial, yet they are surmountable through innovative research and collaborative efforts. The insights gained from studies such as those conducted on the O2 turbine could very well shape the future of tidal energy, guiding its deployment in ways that respect and protect the intricate marine environments upon which it depends.
With a steadfast commitment to addressing ecological concerns while enhancing technological capabilities, the tidal energy sector can pave the way for a cleaner, more sustainable future in energy production. The journey may be complex, yet the destination—a thriving tidal energy industry—holds immense promise for communities and ecosystems alike.

Leave a Reply