A recent study by a team of physicists and engineers from China has introduced a novel approach to gravimetry. Unlike traditional methods that rely on small oscillators or superconducting materials, this new gravimeter operates at room temperature without sacrificing sensitivity or precision.
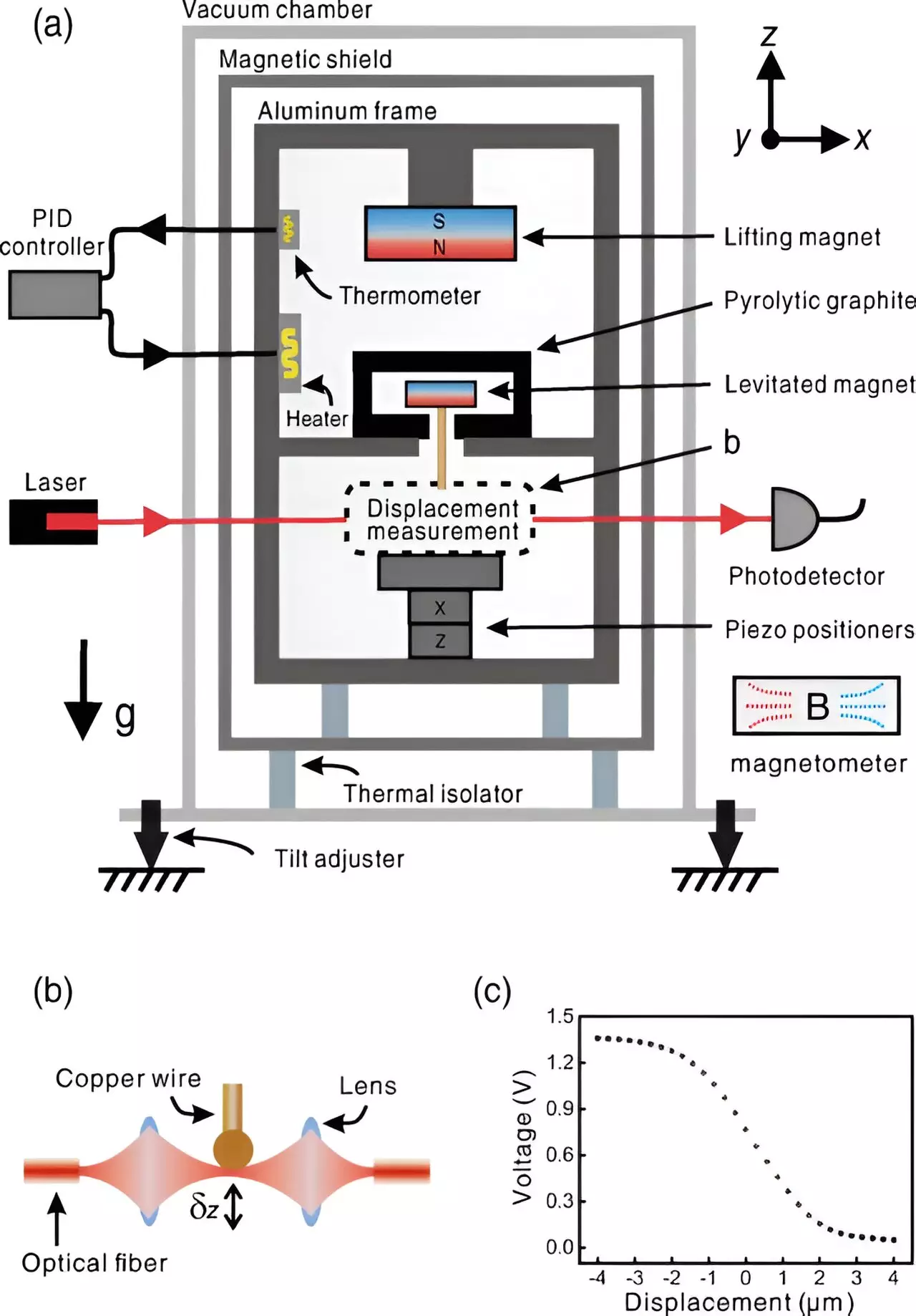
The researchers developed a dual magnet strategy, where a large magnet was placed inside a cabinet with a smaller magnet beneath it. The smaller magnet, encased in a field-repelling graphite shell, levitated due to the opposing magnetism. By adjusting the distance between the magnets, the team could achieve vertical oscillations as low as 1 Hz.
Laser Measurement System
To measure changes in gravity, the team incorporated a wire hanging down from the larger magnet. The movement of the wire, representing shifts in gravitational pull, was monitored using a vertical laser. The laser’s intensity varied as the wire blocked its path, allowing the researchers to calculate the amount of gravity experienced by the device accurately.
After testing the gravimeter in a vacuum chamber and collecting data from the moon and sun, the team observed oscillations in gravitational acceleration of up to 10^-7 of the standard value. This level of accuracy demonstrates the potential of their device as a proof-of-concept that can be further refined for increased precision.
Looking ahead, the researchers plan to enhance the physical robustness of the gravimeter to endure transportation between different sites. They anticipate that additional developments and refinements will lead to even greater precision in gravity measurement, opening up new possibilities for research and applications in a wide range of fields.
The innovative approach to gravimetry presented in this study represents a significant breakthrough in the field of gravity measurement. By leveraging dual magnetism and a laser measurement system, the research team has demonstrated the potential for high precision and sensitivity in gravity detection. With further refinement and development, this new technology holds promise for revolutionizing our understanding of gravitational forces and their applications in various scientific disciplines.

Leave a Reply