Excitons, defined as mobile, microscopic, particle-like objects, are being studied by a research group from the U.S. Department of Energy’s Brookhaven National Laboratory in a class of materials known as van der Waals magnets. These materials display unique properties that could potentially pave the way for new technologies based on magnetism. The study, published in the journal Nature Communications, sheds light on the formation and behavior of excitons in nickel phosphorus trisulfide (NiPS3).
Research Details
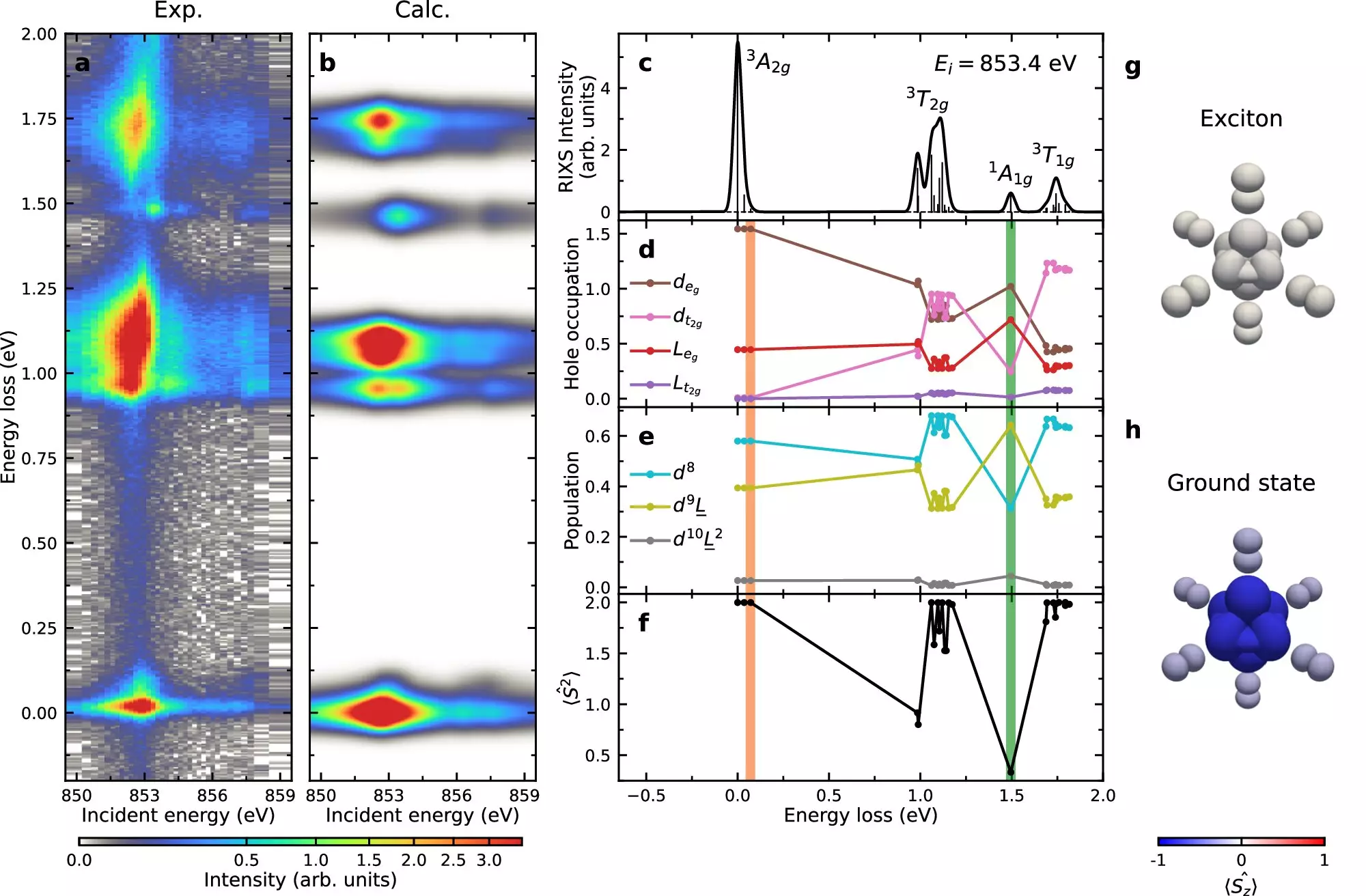
Utilizing the National Synchrotron Light Source II (NSLS-II), a DOE facility at Brookhaven, the researchers investigated NiPS3 using an X-ray technique called resonant inelastic X-ray scattering (RIXS). This technique allowed them to observe the exciton structure and motion within the crystal at a high resolution. The team found that exciton formation and propagation in NiPS3 are influenced by the Hund’s exchange interaction, a physics principle that governs the energy of electron spin configurations.
Findings and Implications
The study revealed that excitons in NiPS3 disperse through the crystal in a manner similar to a double-magnon, a type of spin disturbance. This suggests a strong connection between excitons and the magnetic properties of van der Waals magnets. Understanding this relationship could lead to the development of new technologies based on magnetism, such as advanced information storage systems. As instrumentation and techniques continue to advance, further research in this area is expected to yield even more detailed insights into the behavior of excitons in materials like NiPS3.
The research conducted by the team at Brookhaven National Laboratory provides valuable information about the interaction between excitons and magnetism in van der Waals magnets. By studying materials like NiPS3 using cutting-edge X-ray techniques, scientists are able to uncover the complex behaviors of excitons and their potential implications for future technologies. This study marks an important step towards a deeper understanding of the fundamental properties of excitons and their relationship with magnetism.

Leave a Reply