Quantum computing has been a topic of interest and research for various companies and research institutions. In a recent paper published in Science Advances, researchers from JPMorgan Chase, the U.S. Department of Energy’s Argonne National Laboratory, and Quantinuum have successfully demonstrated a quantum algorithmic speedup for the quantum approximate optimization algorithm (QAOA). This algorithm has shown potential applications in fields such as logistics, telecommunications, financial modeling, and materials science.
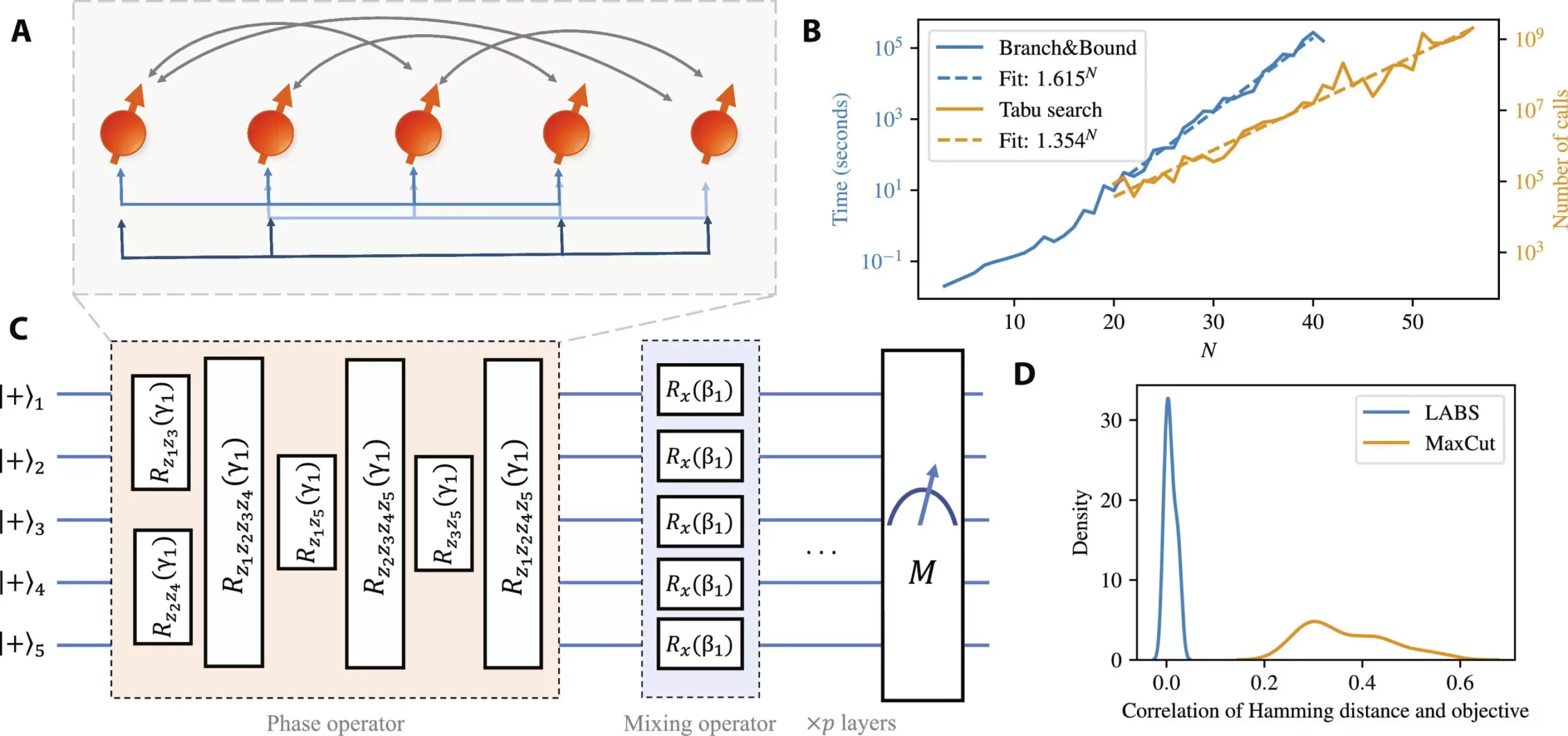
The team aimed to investigate whether a quantum algorithm with low implementation costs could outperform the best-known classical methods. By applying QAOA to the Low Autocorrelation Binary Sequences problem, which holds significance in various fields, they were able to show that as the algorithm tackled larger problems, the time required to solve them grew at a slower rate than that of classical solvers. This demonstrates the potential of quantum computing to provide speedup in solving complex problems efficiently.
Quantum Circuit Simulations
To assess the performance of the quantum algorithm in an ideal noiseless environment, JPMorgan Chase and Argonne collaborated to develop a simulator that could evaluate the algorithm at scale. By efficiently utilizing the DOE petascale supercomputer Polaris at the ALCF, the researchers were able to demonstrate how high-performance computing can enhance the field of quantum information science. This collaborative effort highlighted the importance of leveraging computational resources to advance quantum computing research.
Implementation on Quantum Computers
Taking a step towards practical realization, the researchers implemented a small-scale version of the algorithm on Quantinuum’s System Model H1 and H2 trapped-ion quantum computers. By introducing algorithm-specific error detection techniques, the team managed to reduce the impact of errors on the algorithm’s performance by up to 65%. This implementation showcases the potential of quantum computers to solve complex problems efficiently, paving the way for future advancements in quantum computing technology.
The successful collaboration between JPMorgan Chase, Argonne, and Quantinuum highlights the importance of partnerships in driving innovation in quantum computing. The results of this research experiment would not have been possible without the cutting-edge technology provided by Quantinuum’s H-Series Quantum Computer. The flexibility and quality of the quantum computers used in this study have set a new standard in the field, enabling researchers to conduct groundbreaking experiments in quantum computing.
The demonstration of quantum algorithmic speedup for the QAOA algorithm marks a significant advancement in the field of quantum computing. By showcasing the potential applications of this algorithm in various fields, the research opens up new possibilities for solving complex problems efficiently. The collaborative effort between industry leaders and research institutions underscores the importance of partnerships in driving innovation and pushing the boundaries of quantum computing technology.

Leave a Reply